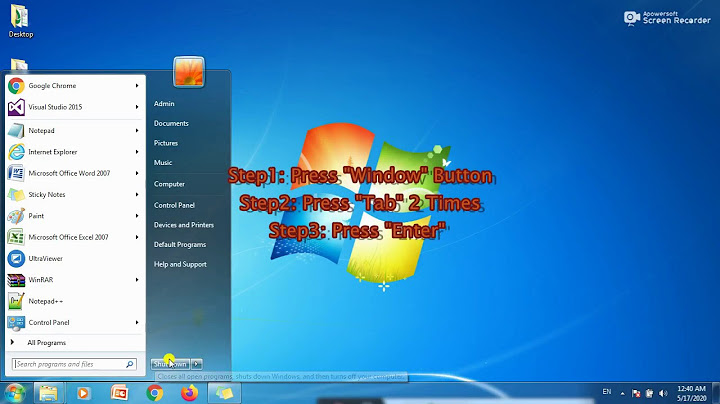
Updated: 08/16/2021 by Computer Hope Show
 An input device is any hardware device that sends data to a computer, allowing you to interact with and control it. The picture shows a Logitech trackball mouse, which is an example of an input device. The most commonly used or primary input devices on a computer are the keyboard and mouse. However, there are other devices that input data into a computer.
Note Although OMR cards and punch cards contain data, they are not considered input devices by themselves. It is the readers that interpret the cards that are considered an input device. Every computer comes with a keyboard and a mouse (touchpad with laptop), which are considered input devices. As far as other input devices, it depends on what was included with your computer and what's connected to the computer. The best method of determining all of the input devices your computer has is to go through the list above. What does an input device send to a computer?What an input device sends (inputs) to a computer depends on the device. Additionally, all input devices send data from the device over a cable or wireless transmission to the computer. For example, as you move a computer mouse, the data sent to the computer is the X-Y axis movements used to display the mouse cursor on the screen. You can see a live example of this on our x-axis definition. Why does a computer need an input device?Today, input devices are important because they are what allows you to interact with and add new information to a computer. For example, if a computer had no input devices, it could run by itself but there would be no way to change its settings, fix errors, or other various user interactions. Also, if you wanted to add new information to the computer (e.g., text, command, document, picture, etc.), you wouldn't be able to do so without an input device. Input devices for physically challenged usersIn addition to the list mentioned above, other specially designed input devices are designed for the physically challenged. Below is a list of examples of these devices.
Hardware terms, HID, Input, Input/output device, Keyboard terms, Mouse terms, Output device, Pointing device Input devices are peripherals used to provide data and control signals to a computer. Input devices allow us to enter raw data for processing. There are many examples of input devices, each with their own benefits and drawbacks. Jump to a section on this page:
Information about a range of sensors can be found on our Sensors page. MouseWhat is a mouse?A mouse is an input device that allows you to control the coordinates and movement of the onscreen cursor/pointer by simply moving the mouse across a flat surface with your hand. Items can be selected or moved using the left mouse button, whilst the right button usually displays additional menus. Most mice are now optical which means they use a laser to detect and track movement across the surface. Mice can be wired or wireless. Typical applications for a mouse
Benefits of a mouse
Drawbacks of a mouse
TrackballWhat is a trackball?A trackball is an input device used to control a pointer/cursor. Unlike a mouse, the device stays stationary whilst the user moves the ball within its socket. Trackballs can be stand-alone devices or combined into a keyboard or control panel. Some people prefer using a trackball over a mouse as they believe it gives them a finer degree of control over the pointer. They are also handy for people with limited hand motor skills as they are less demanding then a mouse. Typical applications for trackballs
Benefits of trackballs
Drawbacks of trackballs
Keyboard What is a keyboard?Keyboards are input devices that allow the entry of data and commands by simply pressing down keys on the keyboard. Keyboards are a common place input device, often used alongside a mouse. They can be wired or wireless. Typical applications for keyboards
Benefits of keyboards
Drawbacks of keyboards
Concept KeyboardWhat is a concept keyboard?A concept keyboard is an input device similar to a traditional keyboard but each key/button is identified by an image. The images are chosen to symbolise the command/option each key represents. E.g. In a fast food restaurant, the concept keyboard belonging to the cashier’s till may use images to represent each type of meal available to purchase, or each size of drink that can be chosen. Traditional ‘overlay’ concept keyboards are now being replaced with virtual concept keyboards using touchscreens. Typical applications for concept keyboards
Benefits of concept keyboards
Drawbacks of concept keyboards
MicrophoneWhat is a microphone?Microphones are input devices that take analogue sound waves and converts them into electrical signals, suitable for a computer to understand. Microphones play an important role in speech recognition, a technology that is gaining in popularity and usage. Typical applications for microphones
Benefits of microphones
Drawbacks of microphones
Digital CameraWhat is a digital camera?Digital cameras are input devices that capture images (and sometimes video) digitally. Digital cameras use an image sensor chip to capture the image, rather than the film used by a traditional camera. The images recorded on a digital camera are stored on memory cards, although some may have a limited amount of external memory of its own. Digital cameras feature an LCD screen which allow you to preview and review your images, plus change menu settings. Typical applications for digital cameras
Benefits of digital cameras
Drawbacks of digital cameras
2D Scanners What is a 2D scanner?2D scanners perform the task of turning a 2D document or image into a digital file. They come in two varieties, flatbed or handheld. Some printers have inbuilt flatbed scanners. The functionality of 2D scanners is enhanced when combined with OMR and OCR software. For example, OCR software can convert scanned in text into a computer readable form. Typical applications for 2D scanners
Benefits of 2D scanners
Drawbacks of 2D scanners
3D Scanners What is a 3D scanner?A 3D scanner is an input device that creates a 3D model of the object scanned. Scanning can be achieved either by using lasers, light, radio waves or x-rays. Typical applications for 3D scanners
Benefits of 3D scanners
Drawbacks of 3D scanners
Test your knowledge of input devices with our quick quiz. Interactive WhiteboardWhat is an interactive whiteboard?Developed long before touchscreens became affordable, interactive whiteboards combine a large touch sensitive board with a projection screen. Interactive whiteboards are versatile input devices, allowing navigation and drawing/writing via your finger or special dummy pens. Typical applications for interactive whiteboards
Benefits of interactive whiteboards
Drawbacks of interactive whiteboards
TouchscreensWhat is a touchscreen?A touchscreen is an electronic visual display that also incorporates an input device that responds to touch. This allows users to select options from a screen by simply touching them. There are three main types of touchscreen technology, all of which are outlined below. Typical applications for touchscreens
Benefits of touchscreens
Electrical current is sent from the four corners of the screen. When your finger (or stylus) touches the screen, the current changes. This allows the location of the touch to be calculated.
Resistive touchscreens use multiple layers of material that transmit electrical currents. When the top layer of the screen is pushed/touched into the bottom layer the electrical current changes. This allows the location of the touch to be found.
Infra-red touchscreensInfra-red touchscreens use a pattern of LED infra-red beams to form an ‘invisible’ grid on the screen. Sensors detect where the screen has been touched by detecting a break in the infra-red beams. The position of touch is then calculated.
Barcode ReaderWhat is a barcode?A barcode is a machine readable code represented by an image consisting of black and white lines. The lines in a barcode relate to numbers 0 to 9. Black and white surfaces reflect light differently, with black bars reflecting less light than white bars. Sensors are used to capture the amount of light reflected and the different reflections are converted to binary values. This is how the scanner is able to identify the corresponding digits from the lines. Scanning a barcode is easier and faster than typing in the series of numbers by hand. A barcode identifies an item, it does not store any further information relating to it, this is achieved by looking up the value in a database. When used in retail, you no longer need to trust sales staff to remember or key in the prices of products. Accurate receipts can be given to customers whilst the business benefits from reliable sales and stock reports. Prices can be changed immediately without changing any barcodes. Typical applications for barcodes
Benefits of barcodes
Drawbacks of barcodes
QR Code ReaderWhat is a QR code?A QR code is a computer generated pattern capable of holding a modest amount of data. This data is accessed when the QR code is read by a QR scanner. We often see a smartphone used as the scanning device although this doesn’t have to be the case. QR codes often store simple data such as a URL address, contact information, calendar entries and product details (in factories and warehouses etc). Typical applications for QR codes
Benefits of QR codes
Drawbacks of QR codes
Graphics Tablet What is a graphics tablet?A graphics tablet is an input device that uses a special pen like stylus to allow the user to “hand draw” images into a computer system. This allows artists to draw in a similar way to how they naturally would using pen and paper; something difficult to achieve with a mouse. Graphics tablets can also be used for day to day data input and are especially useful for capturing handwritten signatures. Some graphic tablets also incorporate an LCD screen for a more realistic experience. Typical applications for graphics tablets
Benefits of graphics tablets
Drawbacks of graphics tablets
Test your knowledge of input devices with our quick quiz. Related TheoryRelated Quizzes
|

zusammenhängende Posts
Werbung
NEUESTEN NACHRICHTEN
Toplisten
#1
#2
#3
Top 8 zeichnen lernen für kinder online 2022
1 Jahrs vor#4
Top 8 schluss machen trotz liebe text 2022
1 Jahrs vor#5
#6
Top 8 wie fallen calvin klein sneaker aus 2022
1 Jahrs vor#7
Top 5 mi band 3 schrittzähler einstellen 2022
1 Jahrs vor#8
#9
Top 9 sich gegenseitig gut tun englisch 2022
1 Jahrs vor#10
Werbung
Populer
Werbung

Urheberrechte © © 2024 wiewird Inc.